The healthcare industry is one of the most complicated systems in the world, with regular changes and updates. Managing patient care, scheduling, billing, insurance claims, healthcare compliance, and financial transactions can become overwhelming as time goes on. This is where medical billing services come in. Medical billing services simplify the process of billing and payment, ensuring that healthcare providers can focus on what they do best – taking care of their patients.
Medical billing is the process of submitting and following up on claims with health insurance or other companies in order to receive payment for services rendered by healthcare providers. It involves translating medical procedures, diagnoses, and treatments into standardized medical billing codes, which are then used to create invoices or claims for insurance reimbursement.
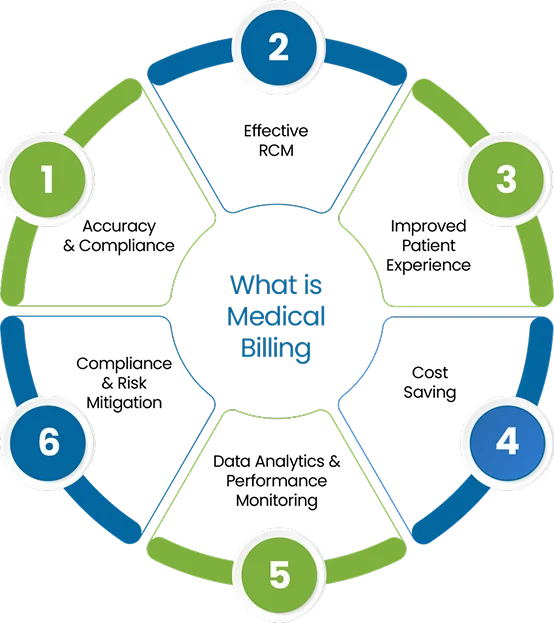
The process includes verifying patient insurance, ensuring accurate coding, submitting claims, and managing any denials or rejections. Effective medical billing ensures that healthcare providers are compensated for their services in a timely manner while complying with regulatory standards. It also helps in avoiding errors that could lead to claim denials or delays.
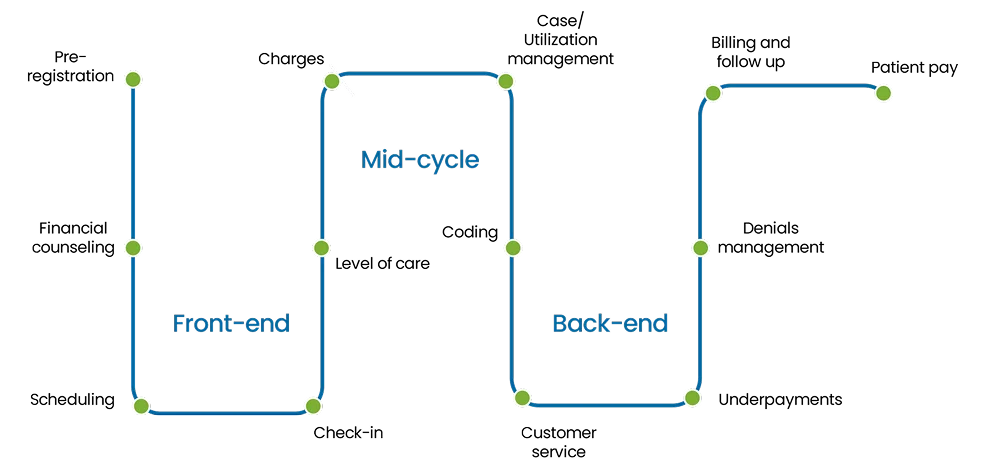
Medical billing works by translating healthcare services into standardized codes, submitting claims to insurance companies or patients, and ensuring proper reimbursement for services provided. The medical billing process broken down into three stages:
There are three main types of medical billing systems that facilitate both healthcare professionals and patients with distinct characteristics within various health care practices.
Let our team help you implement best billing practices that increase collections and reduce administrative frustration.
Clean Claims
HIPAA Compliance
HIPAA Compliance
Collection Ratio
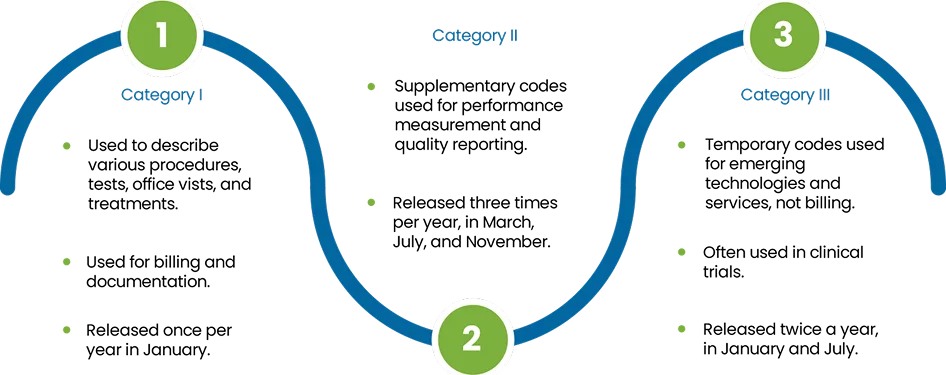
Medical billing used three main types of standardized codes to ensure accurate billing and reimbursement from insurance providers. Which are as follow:
CPT codes are a standardized set of codes used by healthcare providers and payers to document and report medical services, routine check-ups, surgical procedures, and diagnostic tests. These codes help to render healthcare services provided during a patient visit, making it easier for the insurer to understand the treatment process thoroughly and determine the reimbursement ratio depending on it.
Example: A routine office visit might be coded with a specific CPT code like 99213, which corresponds to an evaluation and management service for an established patient.
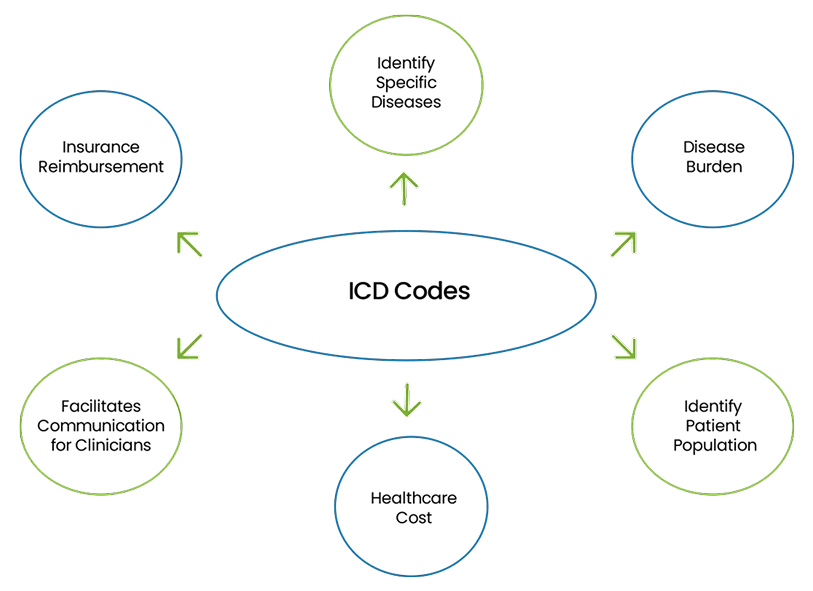
ICD codes are used to classify and code diseases, conditions, and other health-related problems. These codes help identify the reason for a patient’s visit, guiding both medical professionals and insurance companies in understanding the health issue being treated. Additionally, it ensures that the healthcare provider’s diagnosis is properly linked to the services provided, enabling proper reimbursement.
Example: If a patient visits for a knee injury to the lower leg, the ICD code may be range S80-S89, which refers to osteoarthritis of the right knee.
HCPCS codes are a set of codes used primarily for medical services and supplies not covered under the CPT code system, such as durable medical equipment (like wheelchairs, crutches, prosthetics), ambulance services, and certain drugs and medical surgical supplies. DME billing services help ensure that these items and services are billed accurately and reimbursed appropriately, minimizing the risk of claims denials.
Example: A HCPCS code like E0114 is used for crutches, underarm, wood, adjustable height.
| Type | Description | Issued By | Used For |
|---|---|---|---|
| J Codes | Permanent code for drugs dillable under Medicare | CMS | Community and hospital billing for outpatient physician administered drugs |
| C-Codes | Paid under the Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS) | CMS | Hospital-based |
| Q-Codes | Temporary codes for drugs billable under Medicare | CMS | Community and hospital billing for outpatient physician administered drugs |
| S-Codes | Temporary codes for drugs billable under Medicare | BCBS Associations and listed in HCPCS coding set by CMS | Non-Medicare Community and hospital billing for drugs and services |
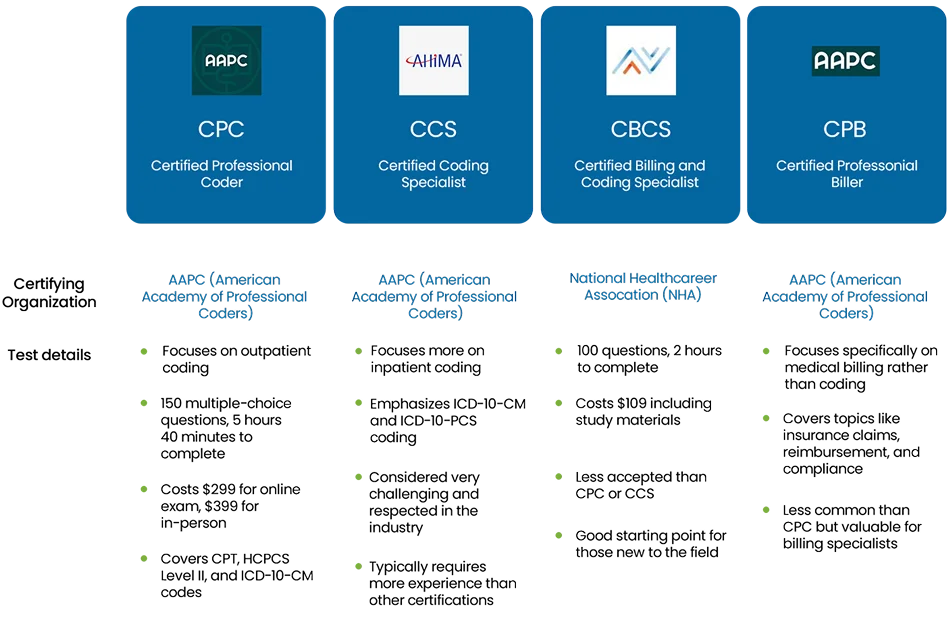
HCPCS codes are a set of codes used primarily for medical services and supplies not covered under These medical codes ensure that the healthcare provider is reimbursed correctly by the insurance company. Accurate coding helps prevent claim denials, reduces administrative errors, and ensures a smoother payment process for both the provider and the patient. Incorrect or incomplete coding can delay payments and lead to financial discrepancies, making it vital to have trained medical coders and billers who understand the complex coding systems. Here are some coding certifications that are often mandatory based on regulatory requirements HCPCS codes help ensure that these items and services are reimbursed appropriately.
The process for medical billing involves coding services, submitting claims, and ensuring timely reimbursement through accurate patient documentation and compliance with regulations. The details for each step are as follows:
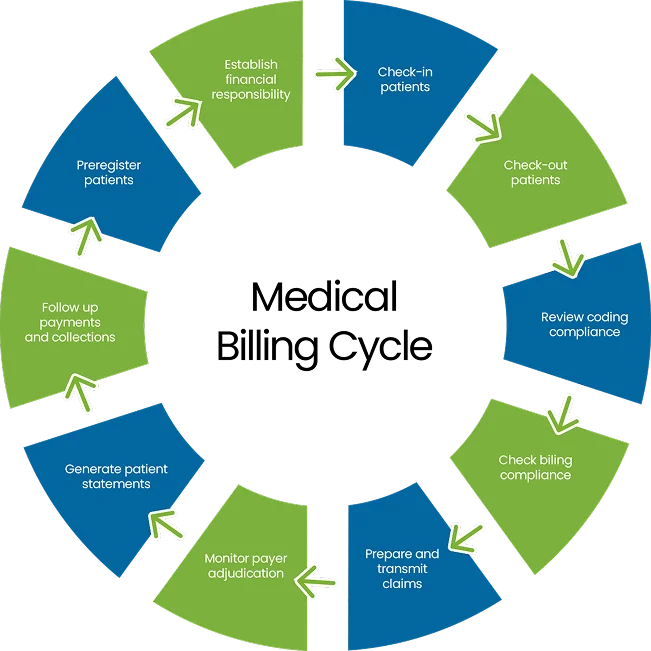
The initial and important step in the medical billing process is patient registration, where essential information is collected, like:
Once the information is gathered, the very next step in the medical billing is to verify the patient insurance eligibility for specific medical services being provided. This include:
After patient registration and insurance confirmation, the next step is coding the services that were provided during the patient visit. This involves translating medical diagnoses, treatments, procedures, and equipment into standardized alphanumeric codes (ICD, CPT, and HCPCS). This step involved:
FYI : Encounter Documentation Essentials
For accurate billing, make sure to document:
Proper documentation is vital to ensure a smooth and clean claim process, as incorrect or incomplete patient information can result in claim denial or delays, while impacting healthcare provider’s cash flow.
Once the services are coded correctly, the medical billing moves on the claim generation and submission to the insurance company. These step involves creating an electronic or paper claim form that include:
Two type of claim submission method used are as follow:
| Claim Submission Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronic Submission | Claims submitted through a clearing house between healthcare providers and insurers. | Faster processing, fewer errors, reduced paperwork. | Requires technology and system setup. |
| Paper Claims | Claims submitted via paper forms (e.g CMS-1500, UB-04). | Can be used if electronic submission is not available. | Slower processing, more prone to errors. |
The accuracy of the claim submission is important. If claims are not submitted correctly or on time, it can delay the reimbursement process or result in claim denials. Electronic submission ensures that claims are received by the insurer faster and with fewer chances of error.
After a claim is submitted, it enters the adjudication phase, where the payer decides the amount of reimbursement ratio. Insurance payer evaluates the claim to determine:
The outcomes of the adjudication process may include:
Once the claim is approved by the insurance company, the payer sends payments, an Explanation of Benefits (EOB), or Electronic Remittance Advice (ERA) to the healthcare provider’s account. The balance that remains after the insurance payment (i.e. the patient’s deductible, co-payment, or coinsurance) is then billed to the patient. Additionally, if the insurance company underpays or the payment is less than expected, the billing department must inquire and resolve any discrepancies. This might involve contacting the insurer to request additional payment or appeal a decision.
Importance: Accurate payment posting is necessary to maintain a clear record of the practice’s revenue. If payments are not recorded properly, it can lead to confusion about the balance, delays in collections, or financial discrepancies. crutches, underarm, wood, adjustable height.
After insurance payments are posted, the next step is patient billing for the remaining balance. The healthcare provider sends a full-detailed statement or bill receipt to the patient for the remaining or outstanding balance after the insurance company has paid. This includes amounts like co-pays, coinsurance, deductibles, and services not covered by insurance. Moreover, keeping a transparent communication with patients regarding their financial responsibility is mandatory for good relationships. The process should involved:
After submitting the claim, it’s necessary to follow up with the insurance company to check the status of the claim and address any issues such as:
The last step included in medical billing is to generate reports under the set KPIs for all the trends in claim denials or payments to maximize the overall financial health of the practice.
| Benefits | Importance |
|---|---|
| Accurate and Timely Payments | Medical billing services help healthcare practices of any size to receive accurate and timely payment for services rendered by submitting accurate and complete claims to insurance companies. |
| Eliminate Errors and Denials | Professional billing services eliminate the chances of claims being denied or delayed by accurate patient documentation and coding, which helps ensure the chances of first-time claim approvals. |
| Improves Cash Flow | By streamlining the billing process and reducing old AR, medical billing services help maintain a healthy cash flow for the providers. |
| Regulatory Adherence | Medical billing services ensure that all billing processes comply with healthcare laws and regulations, including HIPAA, CMS and insurance guidelines, while eliminating the risk of costly penalties. |
| Saves Time and Resources | Outsourcing billing services allows healthcare providers to focus more on quality patient care, while all front-end and back-end tasks are handled by expert medical billers. |
| Cost-Effective | Medical billing software is often more affordable than maintaining an in-house billing team, saving on overhead costs like salaries and other training expenditures. |
| Handles Complex Insurance Plans | Billing services are experienced in managing complicated insurance policies, making it easier for healthcare providers to work with various insurers and plans without confusion. |
| Reduces Administrative Burden | Outsourcing billing services reduces the workload on medical staff, allowing them to focus on other critical tasks rather than dealing with billing and insurance issues. |
| Improves Patient Satisfaction | With an accurate billing process, patients can receive clear and understandable invoices, improving their overall experience and reducing confusion or disputes over charges. |
Compliance and regulations are the most important part in medical billing to ensure healthcare providers adhere to all legal and industrial standards while submitting any claim. Moreover, staying up-to-date with these rules helps prevent costly errors, audits, costly-penalties, and other legal issues while ensuring a timely and accurate payment clearance process.
| Regulation | Details | Applicable To |
|---|---|---|
| HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) | Ensures the patient data confidentiality, integrity, and security of patient personal information. | Healthcare providers, payers, clearinghouses. |
| CMS (Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services) | Oversees compliance with billing policies and guidelines for Medicare and Medicaid. | Providers billing Medicare or Medicaid |
| Medicare & Medicaid Fraud, Waste, and Abuse (FWA) | Requires compliance with specific billing practices and identifies fraud and abuse. | Healthcare providers, insurance companies, government programs |
| False Claims Act (FCA) | Prevents fraudulent billing practices and submission of false claims to government programs (e.g., Medicare, Medicaid). | Healthcare providers, insurers, government contractors |
In medical billing, there are several key payers who are responsible for reimbursing healthcare providers for services rendered to patients. These payers play an important role in ensuring that healthcare providers are compensated for their services. The primary payers in the medical billing process include:
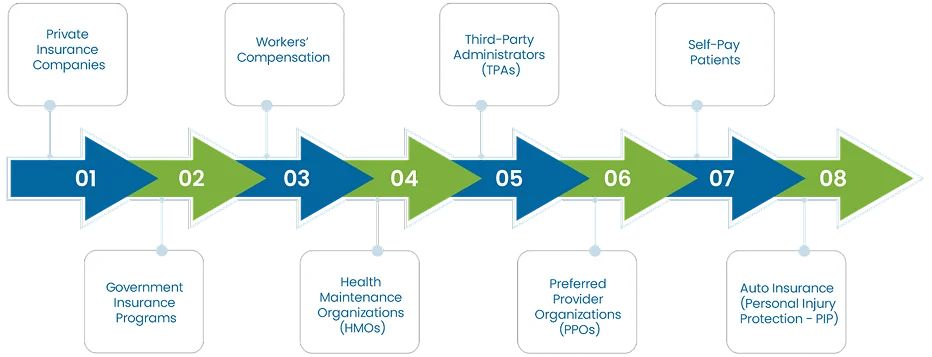
These are for-profit insurance companies that offer health insurance plans to individuals, families, or through employer-sponsored plans. Examples include companies like Blue Cross Blue Shield, Aetna, UnitedHealthcare, and Cigna. Private insurers receive claims from healthcare providers after services are rendered to insured patients. They review the claims based on the patient’s policy, benefits, and eligibility criteria’s and then provide reimbursement according to the terms of the insurance plan. Billing professionals need to understand the specific rules, coding, and reimbursement policies for each private insurer to avoid claim denials and delays.
Government programs represent a significant portion of healthcare coverage in the U.S. Healthcare providers submit claims to these government insurance programs when treating eligible patients. Only provide coverage for certain groups of people such as:
FYI: Medicare, Medicaid, and CHIP have strict billing and documentation requirements, and the reimbursement rates for services are generally lower than those provided by private insurers.
Workers’ compensation is an insurance program that provides coverage for employees who are injured or become ill due to work-related activities. It covers medical expenses, rehabilitation, and lost wages. The billing process for workers’ compensation claims differs from other types of insurance, with specific codes and documentation requirements.
HMOs are a type of managed care plan that provides comprehensive health services to members through a network of doctors, hospitals, and other providers. Patients enrolled in an HMO plan typically need a referral from a primary care physician (PCP) to see a specialist. Healthcare providers must adhere to the HMO’s network requirements, and claims are typically submitted directly to the HMO for reimbursement.
PPOs are another type of managed care insurance plan that offers more flexibility than HMOs. Patients can see any healthcare provider, but they pay less when using providers within the PPO network. Healthcare providers who are part of the PPO network submit claims to the PPO, and the insurer reimburses them according to the patient’s plan. Claims can also be submitted for out-of-network care units, but the patient may have to pay higher costs.
TPAs are independent organizations that process claims for self-insured employers or insurance companies. They manage the administrative functions of insurance claims, such as claim processing and customer service, but do not assume the financial risk of the claims. Healthcare providers will submit claims to the TPA for processing, and they will reimburse the provider based on the employer’s health plan coverage.
Self-pay patients are individuals who pay for healthcare services from their own pocket money, without relying on insurance. This typically applies to those without insurance or those seeking services not covered by their insurance plans. Healthcare providers bill self-pay patients directly for services rendered. In some cases, providers may offer payment plans or discounts for patients paying in full at the time of service.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP) is a part of automobile insurance that covers medical expenses for individuals involved in car accidents, regardless of who was at fault. If a patient is involved in an auto accident, healthcare providers submit claims to the auto insurer under the PIP coverage for treatment related to the accident. PIP insurance often covers medical bills, lost wages, and other expenses resulting from the injury.
Outsourcing your medical billing services can help streamline the billing process, ensuring accurate claims and faster reimbursements. It helps healthcare providers focus on patient care while improving financial performance and maintaining compliance with regulations.
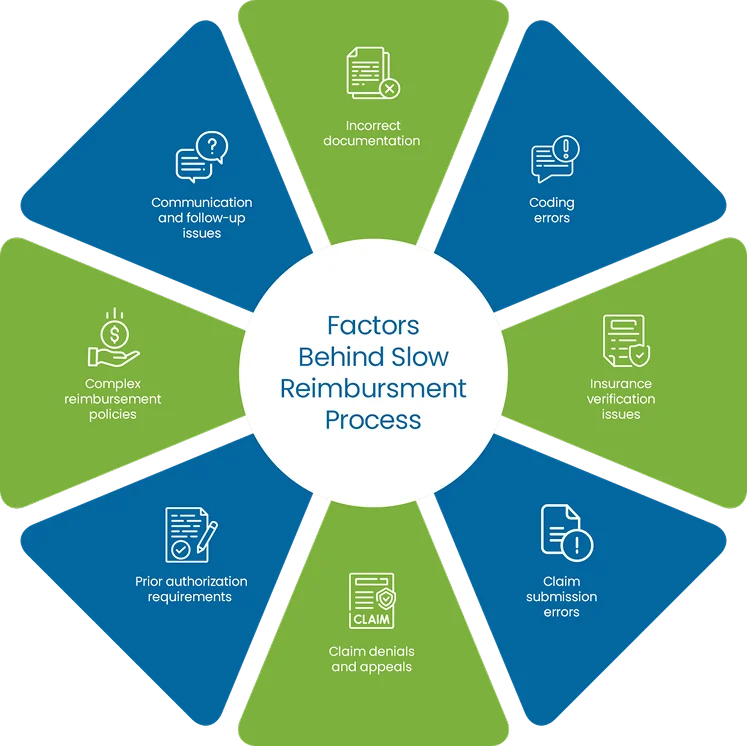
Some of the key challenges in medical billing process are as follow:
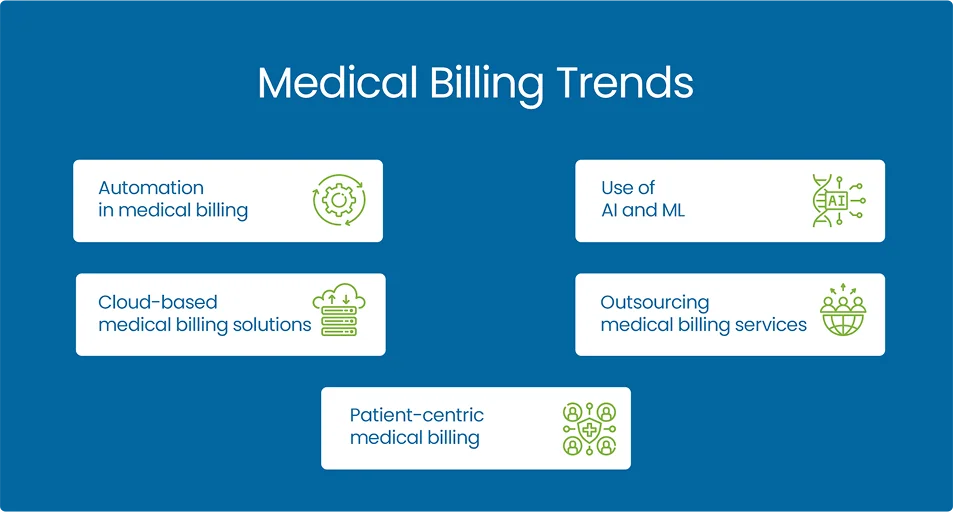
The future of medical billing is in the significant transformation, driven by advancements in cloud-based technology, AI automation, telemedicine’s with evolving healthcare models. As healthcare continues to move toward value-based care models, revenue cycle management systems will need to adapt to ensure accurate reimbursement based on patient outcomes rather than just the volume of services provided.
Listed below are some of the common terms and abbreviations used in medical billing, and as follow in the guide as well:
| Abbreviation | Full Form |
|---|---|
| DME | Durable Medical Equipment |
| BHP | Basic Health Program |
| NPI | National Provider Identifier |
| TIN | Tax Identification Number |
| EMR/EHR | Electronic Medical Records / Electronic Health Records |
| CPT | Current Procedural Terminology |
| HCPCS | Healthcare Common Procedure Coding Systems |
| ICD | International Classification of Disease |
| CLIA | Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments |
| POS | Place of Service |
| ROI | Release of Information |
| ASC | Ambulatory Surgery Center |
| AOB | Assignment of Benefits |
| EGHP | Employer Group Health Plan |
| ABN | Advance Beneficiary Notice |
| ATD | Applied to Deductible |
| RCM | Revenue Cycle Management |
| EOB | Explanation of Benefits |
| ERA | Electronic Remittance Advice |
| HIPPA | Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act |
| CMS | Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services |
| CHIP | Children's Health Insurance Program |
| HMO | Health Maintenance Organization |
| PPO | Preferred Provider Organization |
| EFT | Electronic Funds Transfer |
| PCP | Primary Care Physician |
| PHI | Protected Health Information |
| EIN | Employer Identification Number |
| ACA | Patient Protection / Affordable Care Act |
| FCA | False Claim Act |
| HCFAC | Healthcare Fraud and Abuse Control Program |
| TPL | Third-Party Liability |
By outsourcing your billing services to us, you can expect revenue growth of up to 20%
Medical billing is a critical aspect of the healthcare industry that ensures providers are accurately and timely reimbursed for their services. The process involves patient registration, coding, claim submission, payment posting, and patient billing. By implementing best practices, staying compliant with regulations, and utilizing the right tools, healthcare providers can streamline their billing processes, minimize errors, and enhance their revenue cycle management.
Outsource your medical billing services with MedCare MSO billing specialists. Trust us with your complex claim forms while you can focus on quality patient care. Contact us today to ensure the smooth processing of your claims.
Please provide the following information, so our team can connect with you within 12 hours.
Or call us as 800-640-6409